DAR ES SALAAM, May 31, 2016 – The Consultative Group to Assist the Poor (CGAP), in collaboration with the Financial Sector Deepening Trust (FSDT), launched today the results of a nationally representative survey detailing how smallholder households in Tanzania manage their unpredictable income and financial challenges.

According to the Tanzania Agriculture Census (2010), 98% of farmers in the country are smallholders who work on less than 2 hectares of crop land. Access to basic financial services, mobile phones and other innovative tools can help these families – particularly the most vulnerable, lowest income households – transition out of extreme poverty.
 Jamie Anderson, Financial Sector Specialist of CGAP said: “This national data collection and research could spark better understanding of smallholder households and hopefully lead to financial innovations for this important group of people. The research provides greater insights into how these families transact, make financial decisions and deal with challenges they face on a daily basis.”
Jamie Anderson, Financial Sector Specialist of CGAP said: “This national data collection and research could spark better understanding of smallholder households and hopefully lead to financial innovations for this important group of people. The research provides greater insights into how these families transact, make financial decisions and deal with challenges they face on a daily basis.”
The results of the study were released at an event held in Dar es Salaam. CGAP, a financial inclusion think tank housed at the World Bank, research firms FSDT and InterMedia and a global strategy consulting firm, Bankable Frontier Associates (BFA), were among the organizers and panelists.
 Mwombeki Baregu, Head of Rural and Agriculture Finance, FSDT said: “Smallholders are the backbone of rural Tanzania and as such, their engagement in the financial sector is very important. Through this forum we want to discuss how to better service smallholder farmers to provide them with the products and services they need and want. Financial diaries and surveys give us insights into these needs and wants and what we will try to do is use them to develop solutions.”
Mwombeki Baregu, Head of Rural and Agriculture Finance, FSDT said: “Smallholders are the backbone of rural Tanzania and as such, their engagement in the financial sector is very important. Through this forum we want to discuss how to better service smallholder farmers to provide them with the products and services they need and want. Financial diaries and surveys give us insights into these needs and wants and what we will try to do is use them to develop solutions.”
The main goals of the data are to provide a useful and reliable evidence base for those working in agricultural finance; equip providers, policymakers and funders with important information about the financial needs of smallholder households; and catalyze conversations about relevant strategies and solutions.
Highlights of the survey include:
- Working in a robust agricultural sector, there are opportunities for experienced farmers in Tanzania – 62% of smallholders are over 40 years old – to build and expand their business. However, the next generation of farmers in Tanzania is uncertain and facing many challenges. About 13 percent of smallholders in Tanzania are under 30 years old. Many live in extreme poverty, depend on their land and have few other income sources or financial tools.
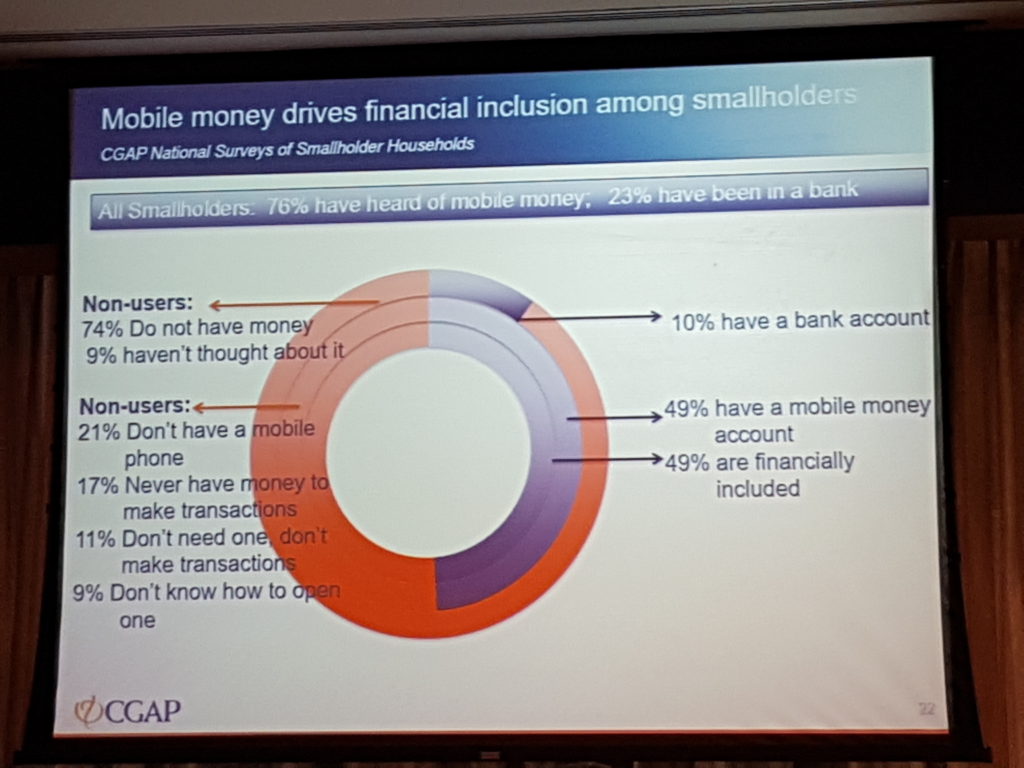
- Mobile money is an entry point for broader financial services. Nearly half of smallholder farmers (49%) have a mobile money account and this tool can be expanded to offer other more sophisticated financial options. Some smallholders are using mobile money for more advanced services such as savings and merchant and service payments. Providers have the opportunity to offer more and better products to this growing group of customers.
- Major advances in financial inclusion will be driven by solutions for the lowest income smallholder families who make up a third of the smallholder sector in Tanzania. This group lacks knowledge of mobile phones, providers or banks and they are not aware of the benefits of financial services. Providing relevant financial solutions that address the priorities and needs of these smallholder families is key to breaking the financial exclusion barrier.


